Getting Started
Welcome to TANGO! This guide will walk you through the basics of using our platform in two ways: through the user-friendly Showcase and the powerful developer API. In this section you will find step-by-step instructions to interact and get results from AI models hosted on TANGO.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure you have:
- A TANGO account (if you don’t have one, request it from your workspace supervisor—the person responsible for your team)
- Your login credentials (email, password, workspace)
If you don’t know who your workspace supervisor is, contact support via the Support section.
Core Concepts
Before you begin, it helps to understand three key terms in TANGO:
- Model: An AI model trained to perform a specific task.
- Session: A context for your interactions with a model. Think of it as a conversation thread where you can send multiple requests (invocations) and maintain context.
- Invocation: The act of sending data to the model and getting a result.
The TANGO Showcase
The TANGO Showcase is a web application that allows users to interact with AI models hosted on the TANGO platform without needing to write any code. It provides a user-friendly interface for exploring, testing, and utilizing the AI models registered on your workspace.
-
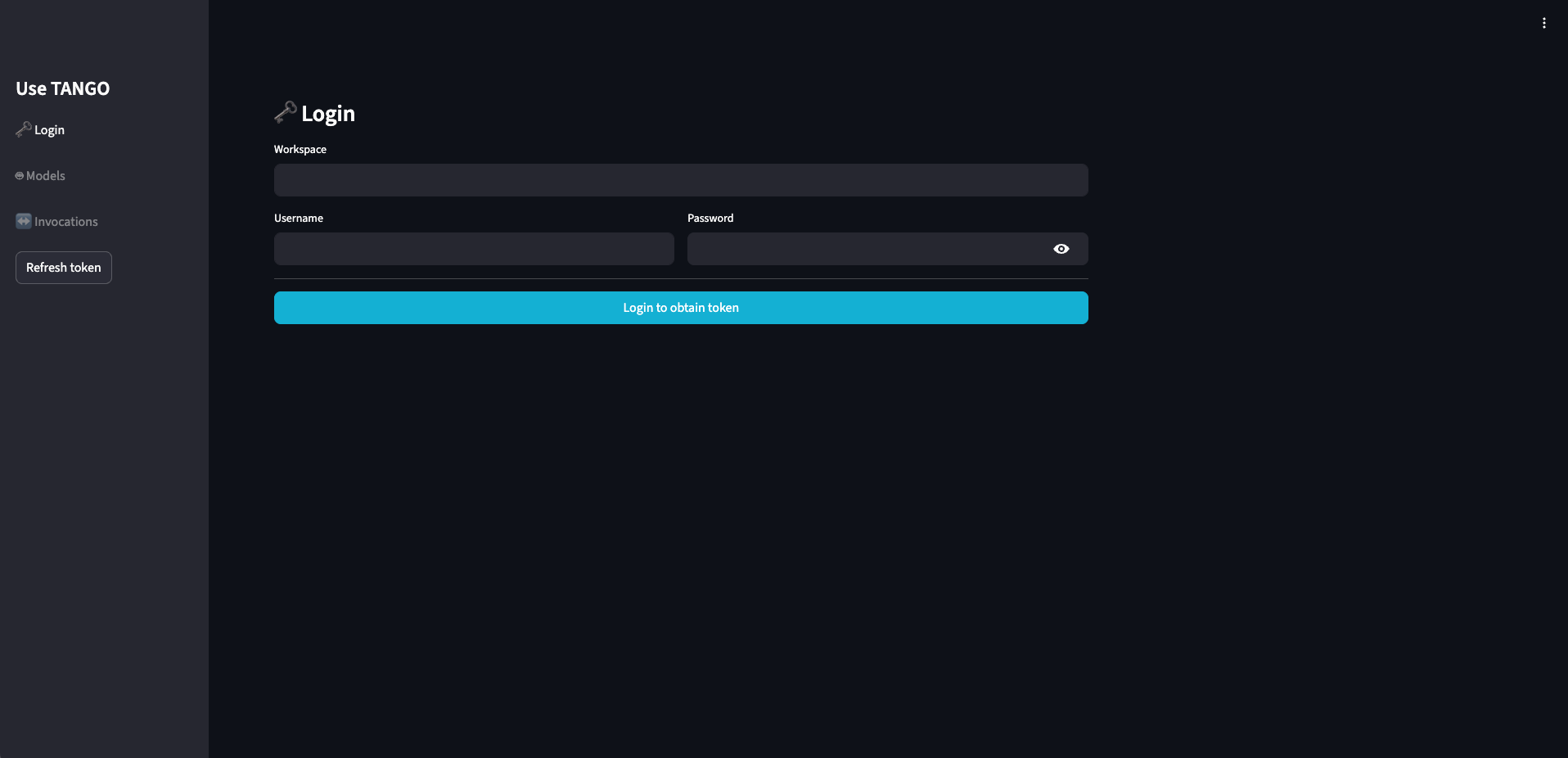
Log In: Navigate to the Showcase URL and log in with the credentials provided by your workspace supervisor.
-
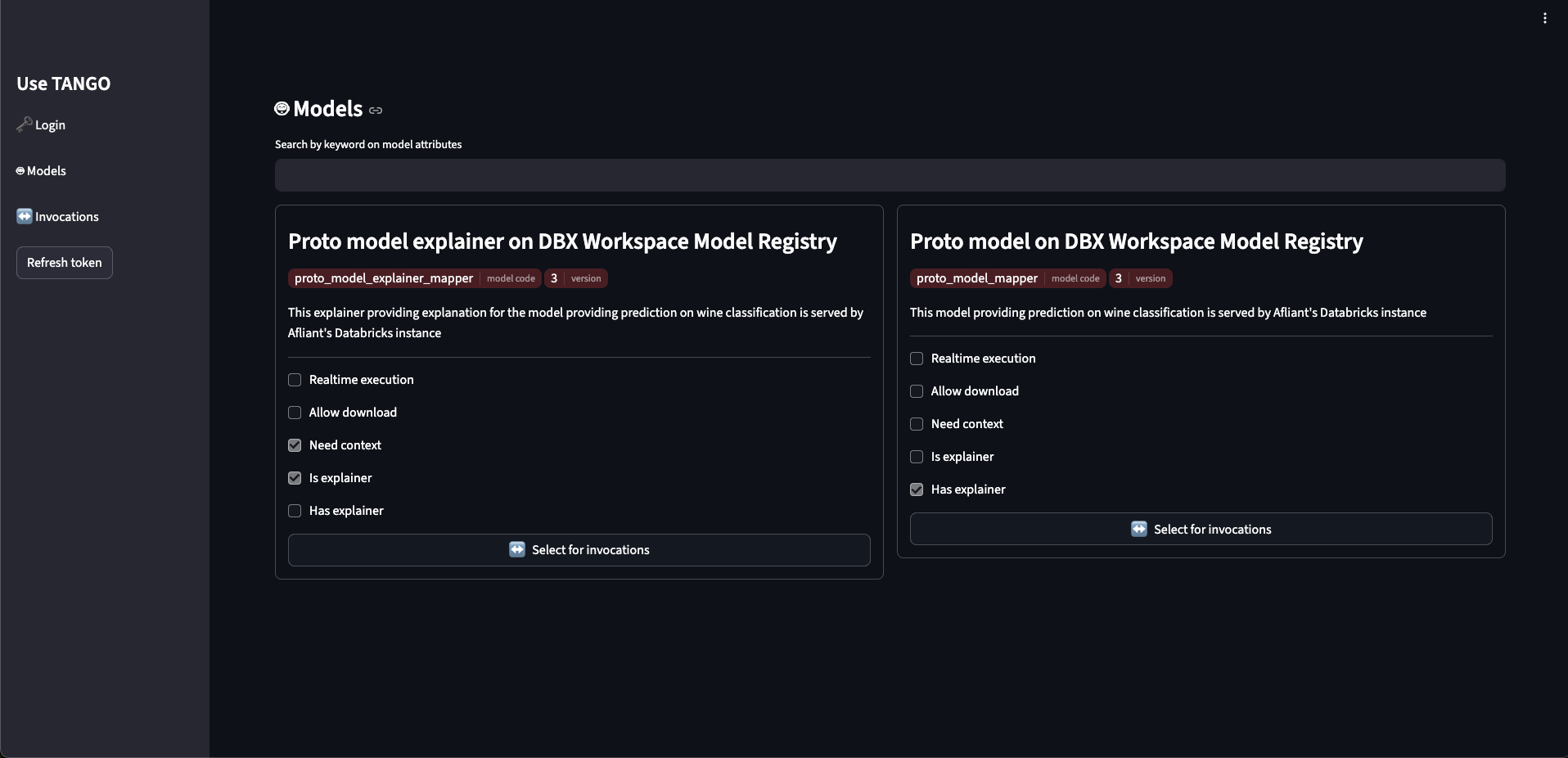
Select a Model: From the sidebar, click on Models. This shows all the AI models available in your workspace. Select the one you want to use.
-
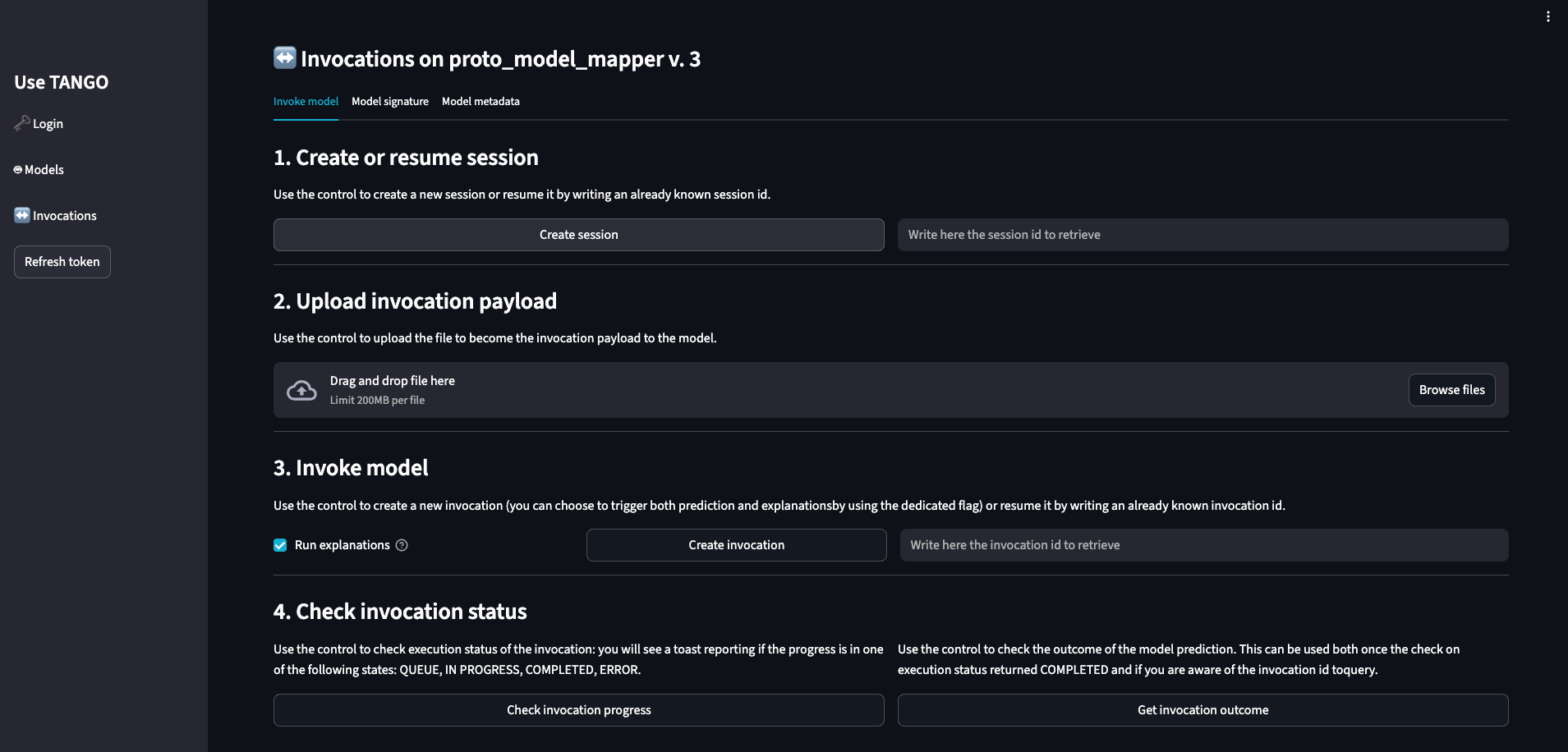
Create a Session: You'll be taken to the model's interaction page. First, click Create Session to start your interaction. A new Session ID will appear in the field.
-
Create an Invocation: Enter your input data into the required fields and click Create Invocation. This sends your request to the model.
-
Get the Result: An Invocation ID will appear. The status of your request can be checked using the dedicated button. Once the status changes to COMPLETED, you can view the model's output by clicking the Get Invocation outcome button.
In case you selected the Run explanation option when creating the invocation, you will receive an additional invocation ID for the explanation request.
Indeed, instead of just the invocation ID, you will see a dropdown menu to select which invocation you want to check the status for and retrieve the result.
The explanation runs asynchronously and automatically after the prediction invocation is completed, therefore you will see it only after the prediction status is COMPLETED.
You can check its status and retrieve the explanation in the same way as for the prediction invocation.
If you have already executed a prediction, you can insert an existing session ID and invocation ID to retrieve previous results.
The TANGO API
You can interact with the TANGO platform programmatically using the TANGO API. The API allows you to perform various operations, such as authenticating, listing models, querying models, and handling sessions and invocations. This guide assumes you are familiar with using curl and REST APIs.
1. Authentication
First, you need to obtain an access token to authenticate your requests. You can obtain it by calling the dedicated endpoint and passing the following parameters:
email: your email addresspassword: your passwordworkspace: the workspace you want to access (if you do not know your workspaces, you can omit this field and fetch the list of workspaces you have access to)
curl --location 'https://auth.tango.u-hopper.com/api/auth/token/obtain' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Cookie: language=en-us' \
--data '{
"email": "<set-me>",
"password": "<set-me>",
"workspace": "<set-me>"
}'
Typical response:
{
"access": "<access_token>",
"refresh": "<refresh_token>"
}
If you do not know your available workspaces, omit the workspace field and retrieve the list with:
curl --location 'https://auth.tango.u-hopper.com/api/auth/workspace' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>'
2. List Models
Once you have the access token, you can list all the models available in your workspace:
curl --location 'https://public.tango.u-hopper.com/api/model' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>'
Example response:
[
{
"code": "model-xyz",
"version": "1",
"name": "Model XYZ",
"description": "Image classification",
"metadata": { ... }
},
...
]
3. Create a Session
Create a session for a specific model:
curl --location --request POST 'https://public.tango.u-hopper.com/api/model/<model-code>/version/<model-version>/session' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>' \
--header 'Cookie: language=en-us' \
--data ''
Response:
{
"id": "d290f1ee-6c54-4b01-90e6-d701748f0851"
}
4. Create an Invocation
curl --location 'https://public.tango.u-hopper.com/api/model/<model-code>/version/<model-version>/session/<session-id>/invocation' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>' \
--header 'Cookie: language=en-us' \
--data '{
"type": "PREDICT",
"request": {
"type": "FEATURES",
"body": "<set-me>"
}
}'
The invocation execution is asynchronous, so you will receive an invocation ID to check the status later.
{
"id": "d290f1ee-6c54-4b01-90e6-d701748f0851"
}
5. Get the Result
Check the status:
curl --location 'https://public.tango.u-hopper.com/api/model/<model-code>/version/<model-version>/session/<session-id>/invocation/<invocation-id>/check_progress' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>'
Response:
{
"status": "COMPLETED"
}
Retrieve the result:
curl --location 'https://public.tango.u-hopper.com/api/model/<model-code>/version/<model-version>/session/<session-id>/invocation/<invocation-id>' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>'
In the response, among other fields, you will find the request and response fields containing the input data sent to the model and the output data returned by the model, respectively.
{
"request": {
"body": { "your": "input-data" }
},
"response": {
"body": { "model": "output-data" }
}
}
Technical Documentation
For the full API documentation, see the OpenAPI section.